“The deity of Sringin, Malayala Brahman is also worshipped in most of the Advaitic institutions with which Sri Vidyaranya Swami has been associated in some way or other-as founder or restorer.Shri Vidyaranya’s meeting the Brahmarakshas, Sringin, in the Vindhya forest has been narrated in ‘Vidyaranya-kṛti’ (the opening part of ‘Vidyaranya Kālajñāna’), the ‘Guruvamsa Kavya’ and in the ‘Renukatantra. Srigin is also given the name ‘Malayala Brahman.’ According to available authentic information, there is a ‘Brahma Devaru’, deity in the Kudali Sringeri Matha, located on the bank of the Tungabhadra (in Shimoga district, Karnataka state) where it is understood that Shri Shankaracharya founded an institution owing to unexpected accidental circumstances. The deity of Brahma Devaru is installed in a small mantapa near Sri Vidyashankara Temple. Nitya-puja is being performed to this deity only in the morning. The sankalpa made is as follows: “Sringara Bhatta pujam karishye”. Once in a year Aradana (annual special worship) is being done to this Sringara Bhatta (Brahma Devaru or Malayala Brahman) with sixteen Alankara Brahmins sitting.”(Sri Vidyaranya, The Vidyaranya Vidya Pitha Trust, Hampi, Publication no.3, 1983)
Category: Kudali
Why is Sringeri So called?
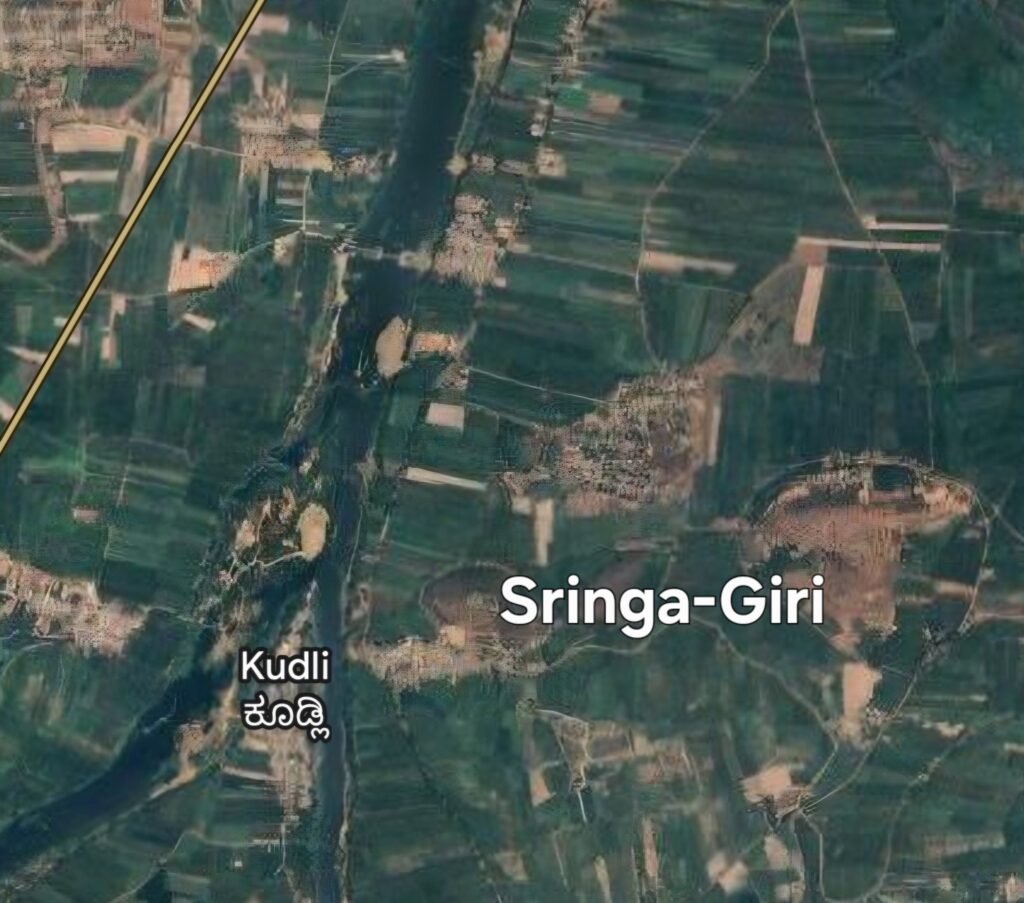
“Why is Sringeri So called?”In Karnataka, many sacred places bear the suffix Sringeri with their name. This name has its origin from Sage Rishyasringa, who performed tapas in the Kudali Kshetra, situated at the confluence of the Tunga and Bhadra rivers. Ancient Inscriptions of Karnataka, studied by B.L.Rice and others, reveal that the sacred hill emerged at this spot due to his intense penance was revered as “Sringa-Giri” in his honor. Over time, the place became known as “Kudali Sringeri”.Source: Epigraphia Carnatica, Vol VI, Inscriptions of Kadur District By B.Lewis Rice, Mysore Government Central Press, Bangalore (1901).
King Sahu’s Intervention to Resolve Spiritual Jurisdiction Disputes Among Kudali, Shankeshvara, and Tunga Mathas (1725 C.E.)
In 1725 C.E., during the reign of King Sahu in the Maratha country, the Swamis of Kudali, Shankeshvara, and Tunga Mathas visited Satara at the king’s invitation in order to resolve their dispute regarding their spiritual jurisdictions amicably. In this important meeting, with the unanimous consent of the Acharyas of Kudali, Shankeshvara, and Tunga Mathas, King Sahu allocated the territories: the northern regions were assigned to Shankeshvara Matha, the southern regions to Kudali Matha, and the Tunga Matha was entrusted with the worship of Shri Sharadamba at their location. Notably, there was no mention of modern texts like the Mathamnaya or Madhaviya during their discussion. This confirms that such ideas were promoted only at a later time.(Sources: History of Sankesvara Mutt, Article published in Indian Patriot, April -June 1912 & Sringeri Matt (Its History) published by (Aviccinna?) Kudali mutt)

Pindari mercenaries destruction of Kudali Sringeri Matha
Why do contemporary historians ignore the tragic event of Pindari mercenaries destroying Kudali Sringeri Matha on December 17, 1790, and hide Tipu’s seizure of the four lakh compensation and fine money sent by the Mahratta Peshwa, to Kudali Sringeri Matha out of fear of excommunication for their wrongdoing?
Q: Who was the first Acharya at Dakshinamnaya Sringeri Matha? What do the various sources indicate?
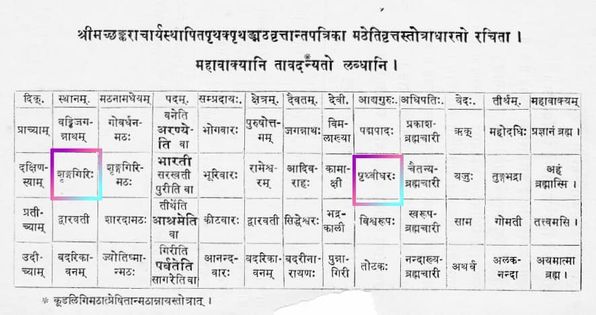
A: Shri Prithvidharacharya’s anointment as the first Acharya of the Dakshinamnaya Sringeri Matha, which was established at the confluence of Tunga and bhadra rivers is evident in texts such as Mathamnaya, Guruparampara of Bharati Sampradaya, and Shankaravijaya Churnika (Purva-pithika)


Tracing Tamil Brahmin Migration : Sankarite Institutions, Sri Vidyatirtha, and Settlements in Mysore’s History
The Historical survey records published by the Mysore Government provide fascinating insights into the migration and settlement of Tamil Brahmins from Tanjore and Kanchipuram regions, near the Sankarite institutions on the Tunga and Tungabhadra rivers (Tunga Sringeri and Tungabhadra -Koodali Sringeri mathas).
In the Quarterly journal of the Mythic Society, while reviewing the 1931 Annual Report of the Archaeological Survey of Mysore, there is an interesting observation that Sri Vidyatirtha also hailed from the Tamil Brahmin community of Choladesa (Tanjore) in his earlier life.
“… Hale Sringeri Village is about two furlongs to the west of Sringeri with about one Brahman and twenty other houses. A small mud shrine contains the old Vidyasankara Linga, about six feet high. The Vidyasankara image is 1½ ft. high in Yoga-mudra with a sannyasi disciple on either side. Compared with this, it will be clear that the image to which I have referred in my article on “An Ancient Image at Hampi ” may not be that of Vidyasankara.
In his notes on Vidyaranyapura, Dr. Krishna says that “Vidyaranya also must have been a Karnataka (Kannadiga). But Vidyasankara is said to have been a ‘choli’ (belonging to the Chola-desa of Tamilnadu) since some ‘cholis’ (Tamil Brahmins from Chola desa) have set up his image in the Agrahara.”
This statement is evidently traditional, picked up during the course of enquiries but it deserves further investigation…”
The authenticity of this statement is supported by the ancient Guruparampara records of Sri Kanchi Kamakoti Peetha. These records state that Sri Vidyatirtha, the 51st Acharya of Sri Kanchi Matha, originated from Bilvaranya kshetra of the Chola desa. His successor, Sri Sankarananda, the 52nd Acharya hailed from Madhyarjuna kshetra (Tiruvidaimaruthur) in the Chola country.
(Reviews : Archaeological Survey of Mysore – Annual Report for 1931 – The Quarterly Journal of the Mythic Society.)

Guruparampara of the Bharati line of Sanyasins

Dr. Hultzch in his Report on the Search for Sanskrit Manuscripts in Southern India, Part II printed by the Government Press, Madras, 1905, refers to a Guruparampara of the Bharati line of Sanyasins and gives the Guru Parampara Vide No. 21461.
This manuscript was also found in the collection of the manuscripts made by a Pandit of the Tanjore Palace. This list gives the names of 30 Acharyas.
According to this Guruparampara Stotra, Sri Sankaracharya established a matha at the Tungabhadra (Kudali) sangama kshetra and anointed Sri Prithvidhara Bharati as its first Acharya. Later, Sri Sankaracharya visited Kanchi where He consecrated Sri Kamakshi Devi and attained the final Bliss.
Sri Sacchidananda Saraswati of Hole Narasipur in his Sri Sankara Bhagavatpada Vrithantha Sarvaswa raised a doubt about the 5th & 6th verses and that their reliability would be clear if it was known who the author of this Guruparampara stotra was.
It is surprising, an erudite scholar like Sri Sactchidananda Saraswati didn’t know the fact that even before Dr.Hultzh, this Guruparampara list was noticed by K.B.Pathak of Belgaum in 1882. According to him Atmananda was the author of this Guruparampara list.
Here’s an Excerpt from K.B. Pathak’s article published in the Indian Antiquary journal:
“I have lately come across a manuscript which gives the date of Samkaracharya. The manuscript belongs to Mr. Govinda Bhata Yerlekara of Belgaum. It is a small one, consisting of three leaves only, written in Balbodh characters.
It begins thus :
श्री त्र्यंबकेश्वरायनमः
नमामि शंकराचार्यगुरुपादसरोरुहं ।
यस्य प्रसादान्मूढोपि सर्वज्ञोऽहं सदास्म्यलं॥
श्रीशंकराचार्यनवावतारं वेदान्तशारीरकभाष्यकारं।
चकोरचाकोरकचंद्रिकाणां श्रीशंकराचार्यगुरुं नमामि॥
आदौ शिवस्ततो विष्णुस्ततो ब्रह्मा ततः परं।
वसिष्ठाख्यस्तथा शक्तिस्तत: पाराशरः स्मृतः॥
ततो व्यासः शुकः पश्चाद् गौडपादाभिधस्तथा।
गोविंदार्यगुरुस्तस्मात् शंकराचार्यसंज्ञकः॥
The manuscript next says that Samkara established his matha on the banks of the Tumgabhadra, appointed Prithvidhara to be the head of it, conferred upon him the title of Bharati, and,
आगत्य स्वेच्छया कांचीं पर्यटन्पृथिवीतले ।
तत्र संस्थाप्य कामाक्षीं जगाम परमं पदं ॥
Then follow the names of his successors. We next come to a minute description of the mathas established in various parts of India. Then follows the guru parampara or the succession of teachers…”
– K.B.Pathak, B.A. Belgaum High School (June,1882)
Royal Elephant Offerings to Kanchi and Sringeri (Kudali) Shankaracharyas
In the historical epistles dating back to the 18th and 19th centuries, we find accounts of the Travancore kings presenting elephants named “Padmanabha” as offerings to the revered Jagadguru Shankaracharyas of Shri Kanchi Kamakoti Peetham.
Additionally, in the records of the Mysore State Government for the year 1941-42, there are detailed entries of the government offering two elephant calves to Shri Kanchi Kamakoti Peetham Jagadguru Shri Shankaracharya Swamigal Srimatham Samsthanam and Jagadguru Shri Sringeri (Tungabhadra-Kudali) Shankaracharya Swamigalavaru Srimatham Samsthanam as a humble contribution.




Tungabhadra Sringeri (Kudali) matha established by Jagadguru Shri Shankara Bhagavatpadacharya
In the Bhumika of the book Sareeraka Meemamsa Bhashyam printed and published by Venkateswara Steam Press, Bombay, written by Mahavidvan Kashi Sesha Venkatachala Shastri, son of Pandita Dharmadhikari Shri Venkatasubramania Shastri and grand son of Pandita Dharmadhikari Kashi Sesha Nageshwara Shastri of Mysore, the following observation was made in Sanskrit about the Tungabhadra Sringeri (Kudali) matha established by Jagadguru Shri Shankara Bhagavatpadacharya.
” अन्यस्मै पुस्तकसन्न्यासाश्रमं ददुः, ततः केषुचिद्दिवसेषु व्यतीतेषूक्तः स्वामी ( = यात्रां गतः स्वामी देशयात्रातः प्रतिनिवृत्य) कूडलीमागत्यैनं वृत्तान्तं ( = महाजनैः शृङ्गेरीमठीय पीठाधिपत्ये स्थापितस्यान्यस्य सन्यासिनो वृत्तान्तं श्रुत्वा राज्यस्थाने (हुजूरास) लेखनस्य निवेदनात्पक्षद्वयमपि तेषामाह्वापनद्वारा विचारितम् । तेन चास्माभिस्तत्रत्यैर्महाजनैर्हठेन दत्तः पुस्तकसंन्यासः सत्यः इत्यवगतम् । तथाप्युपदेशसन्न्यासादिकमनेन देयं, पुस्तकसन्न्यासिभिस्तु ग्रामे (शृङ्गेरीग्रामे) एव स्थित्वा श्रीशारदामातृपूजां कुर्वद्भिर्मठे नियमनिष्ठ्या स्थातव्यं शङ्कराचार्यपरम्परागतैः स्वामिभिः देशसंचारादिकं कुर्वद्भिः कूडल्यां (लग्यां) स्थातव्यम्” इति । इदं (प्राचीन लेख – पुस्तक – राजशासन – पत्रिकालेखाद्यनुरोधेन शशिशेखर दामोदरसङ्केश्वरीय विद्याशालाया अध्यापकेन लिखिते ) “श्रीसंस्थानसङ्केश्वर मठ करवीर व सङ्केश्वरचा इतिहास इति नाम्ना प्रसिद्ध मुद्रितपुस्तके स्पष्टम् |”
Note: That this (Tungabhadra Sringeri) Matha was an independent Matha and that it was entitled to use Addapallaki and other paraphernelia was held in Appeal No.22 of 1847 on the file of the court of Huzur Adalat, Mysore. This order was confirmed by the Commissioner of Mysore, by his order dated 1st June, 1849. In the judgment it has also been quoted that “the Parwana of the Phalguna Bahula, 6 of the year Krodhana is to the effect that the (Tungabhadra Sringeri) Kūḍali Swami should always be on tour and that the (Tunga) Sringeri Swami should ever remain at Sringeri worshipping the deity.”- ‘Extract from the Judgement in Appeal No.22 of 1847 in the Court of the Huzur Adalat, Mysore’.- Sri Sankaracharya And Sankarite institutions by Sri Anantanandendra Saraswati of Upanishad Brahmendra Matha.

FAQ: Jagadguru Acharya of Tungabhadra Sringeri Matha – Tungabhadrateeravasi
Q: Why is the Jagadguru Acharya of Tungabhadra Sringeri Matha revered with the special title “Tunga Bhadra Teeravasi”?
A:According to Mahavidvan Kasi Sesha Venkatachala Sastri of Mysore, the Birudu ” Tungabhadra Teeravasi” is associated with the Matha founded on Pitha in the confluence of Tunga-Bhadra rivers.
“तुङ्गभद्रातीरवासी”
“शृङ्गेर्याः बहुक्रोशदूरवर्तिनि तुङ्गानद्या भद्रानद्याश्च सङ्गमे (कर्नाटकभाषया कूडल्याख्ये) स्थाने मठं निर्माप्य तत्र विद्याधर्मपीठं च संस्थाप्य तत्पीठाधिकारो येन लब्धस्तेन तुङ्गभद्रातीरवासीति सम्पादितं विरुदम् ।”
He founded a Matha and Vidya-dharma Pitha at the confluence of the Tunga and Bhadra rivers (known as Kudali in Kannada), situated many krosas away from (Tunga) Śṛṅgeri. As a result, the Acharyas came to be known by the title “Tungabhadra – Teeravasi.”
(Bhumika- Sareeraka Meemamsa Bhashyam by Kasi Sesha Venkatachala Sastri, Dharmadhikari & Hereditary Court Pandit of Mysore State, Printed By Venkateswara Steam Press, Bombay, 1913)

