Spiritual Jurisdiction and Official Recognition of Sri Kanchi Kamakoti Peetham: Chingleput Collector’s order (1839)
In the context of the Jagadguru Sri Kanchi Kamakoti Sankaracharya Swami’s spiritual jurisdiction over the Jambukeshwaram Devasthanam, the Trichinopoly Tahsildar referenced Chingleput Collector’s order no. 97/6 dated 25-2-1839.
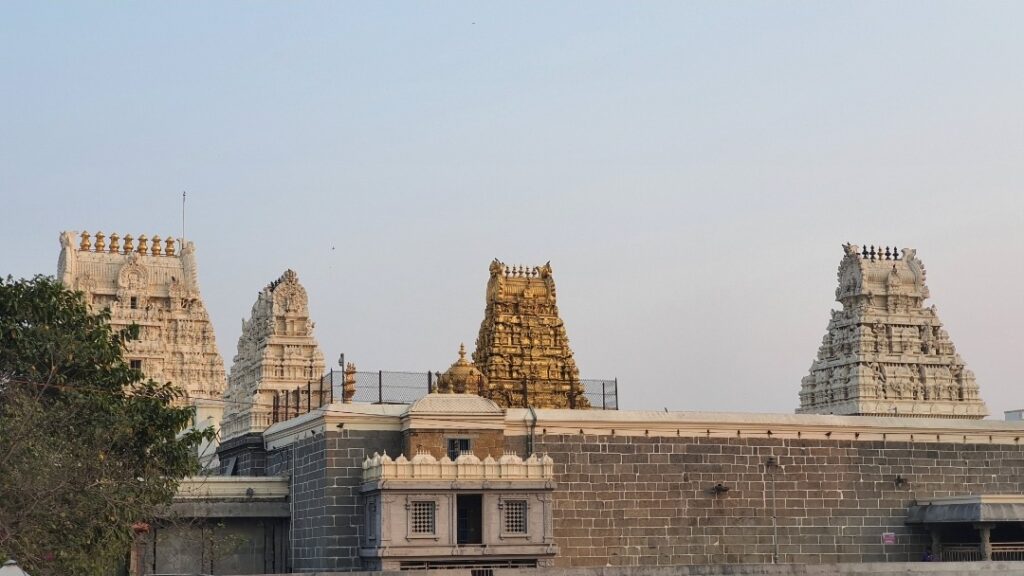
This order specified procedures for the Kumbhabhishekam of Kanchipuram Sri Kamakshi Ambal Devasthanam, which was then under Government management following the relocation of the Kanchi Srimatha to Kumbhakonam.
In 1839, on the basis of the views and requests expressed by the general public, while reporting the Kanchipuram temple’s consecration necessity to the Chingleput Collector, the Kanchipuram Tahsildar prompted the Board of Revenue to release the required funds for carrying out the necessary renovation.
Recognizing the historical ties of Sri Kanchi Kamakoti Peetha with the Kanchi Devasthanam throughout the ages, the Chingleput District Collector immediately ordered the observance of proper formalities in a fitting manner to invite and receive the Kanchi Jagadguru (Sri Chandrasekharendra Saraswati Sankaracharya Swamigal, the 64th Acharya of Sri Kanchi Kamakoti Peetha) for renovating the temple, overseeing of the rituals, and conducting the consecration and immediate release of surplus funds of the Devasthanam from the District Board of Revenue for this purpose. (2/3)
Sri Kanchi Kamakoti Peetha: Tracing Its Spiritual Jurisdiction in Kanchipuram and Jambukeshwaram Through Government Documents from the British Period (Part-2)
Spiritual Jurisdiction and Official Recognition of Sri Kanchi Kamakoti Peetham: Chingleput Collector’s order (1839)
In the context of the Jagadguru Sri Kanchi Kamakoti Sankaracharya Swami’s spiritual jurisdiction over the Jambukeshwaram Devasthanam, the Trichinopoly Tahsildar referenced Chingleput Collector’s order no. 97/6 dated 25-2-1839.
This order specified procedures for the Kumbhabhishekam of Kanchipuram Sri Kamakshi Ambal Devasthanam, which was then under Government management following the relocation of the Kanchi Srimatha to Kumbhakonam.
In 1839, on the basis of the views and requests expressed by the general public, while reporting the Kanchipuram temple’s consecration necessity to the Chingleput Collector, the Kanchipuram Tahsildar prompted the Board of Revenue to release the required funds for carrying out the necessary renovation.
Recognizing the historical ties of Sri Kanchi Kamakoti Peetha with the Kanchi Devasthanam throughout the ages, the Chingleput District Collector immediately ordered the observance of proper formalities in a fitting manner to invite and receive the Kanchi Jagadguru (Sri Chandrasekharendra Saraswati Sankaracharya Swamigal, the 64th Acharya of Sri Kanchi Kamakoti Peetha) for renovating the temple, overseeing of the rituals, and conducting the consecration and immediate release of surplus funds of the Devasthanam from the District Board of Revenue for this purpose. (2/3)